TITLE:
TO PLOT A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP BY STADIA TACHEOMETRY SURVEY
OBJECTIVE:
To introduce the traditional technique of collecting the stadia data such as stadia readings to plot a topographic map.
To Plot a simple topographic map.
THEORY:
Stadia is a method of surveying in which distances are read by noting the interval on a graduated rod intercepted by two parallel cross hairs (stadia hairs or stadia wires) mounted in the telescope of a surveying instrument, the rod being placed at one end of the distance to be measured and the surveying instrument at the other. Principle of Stadia hair method is that the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the base is constant in case of similar triangles.
Fixed Hair Method:
In the fixed hair method, the cross hairs of the diaphragm are kept at a constant distance apart and the staff intercept varies with the horizonta....Show More
TITLE:
TO PLOT A TOPOGRAPHIC MAP BY STADIA TACHEOMETRY SURVEY
OBJECTIVE:
To introduce the traditional technique of collecting the stadia data such as stadia readings to plot a topographic map.
To Plot a simple topographic map.
THEORY:
Stadia is a method of surveying in which distances are read by noting the interval on a graduated rod intercepted by two parallel cross hairs (stadia hairs or stadia wires) mounted in the telescope of a surveying instrument, the rod being placed at one end of the distance to be measured and the surveying instrument at the other. Principle of Stadia hair method is that the ratio of the length of perpendicular to the base is constant in case of similar triangles.
Fixed Hair Method:
In the fixed hair method, the cross hairs of the diaphragm are kept at a constant distance apart and the staff intercept varies with the horizontal and vertical position of the staff with respect to the Theodolite. In this method, the angle at the instrument at A subtended by a known short distance along a staff kept at B is made with the help of a stadia diaphragm having stadia wires at fixed or constant distance apart. The readings are on the staff corresponding to all the three wires taken.
The staff intercept, i.e., the difference of the readings corresponding to top and bottom stadia wires will therefore depend on the distance of the staff from the instrument. When the staff intercept is more than the length of the staff, only half intercept is read. For inclined sight, readings may be taken by keeping the staff either vertical or normal to the line of sight. This is the most common method is tacheometry and the same stadia method generally bears reference to this method.
2. Movable Hair Method
In this method, the staff intercept between the lower hair and the upper hair is kept constant by moving the horizontal cross hairs in the vertical plane. This method is similar to the fixed hair method except that the stadia interval is variable. Suitable arrangement is made to vary the distance between the stadia hair as to set them against the two targets on the staff kept at the point under observation. Thus, in this case, the staff intercept, i.e., the distance between the two targets is kept fixed while the stadia interval, i.e., the distance between the stadia hair is variable. As in the case of fixed hair method, inclined sights may also be taken.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
Theodolite
Tripod
Staff
Hammer
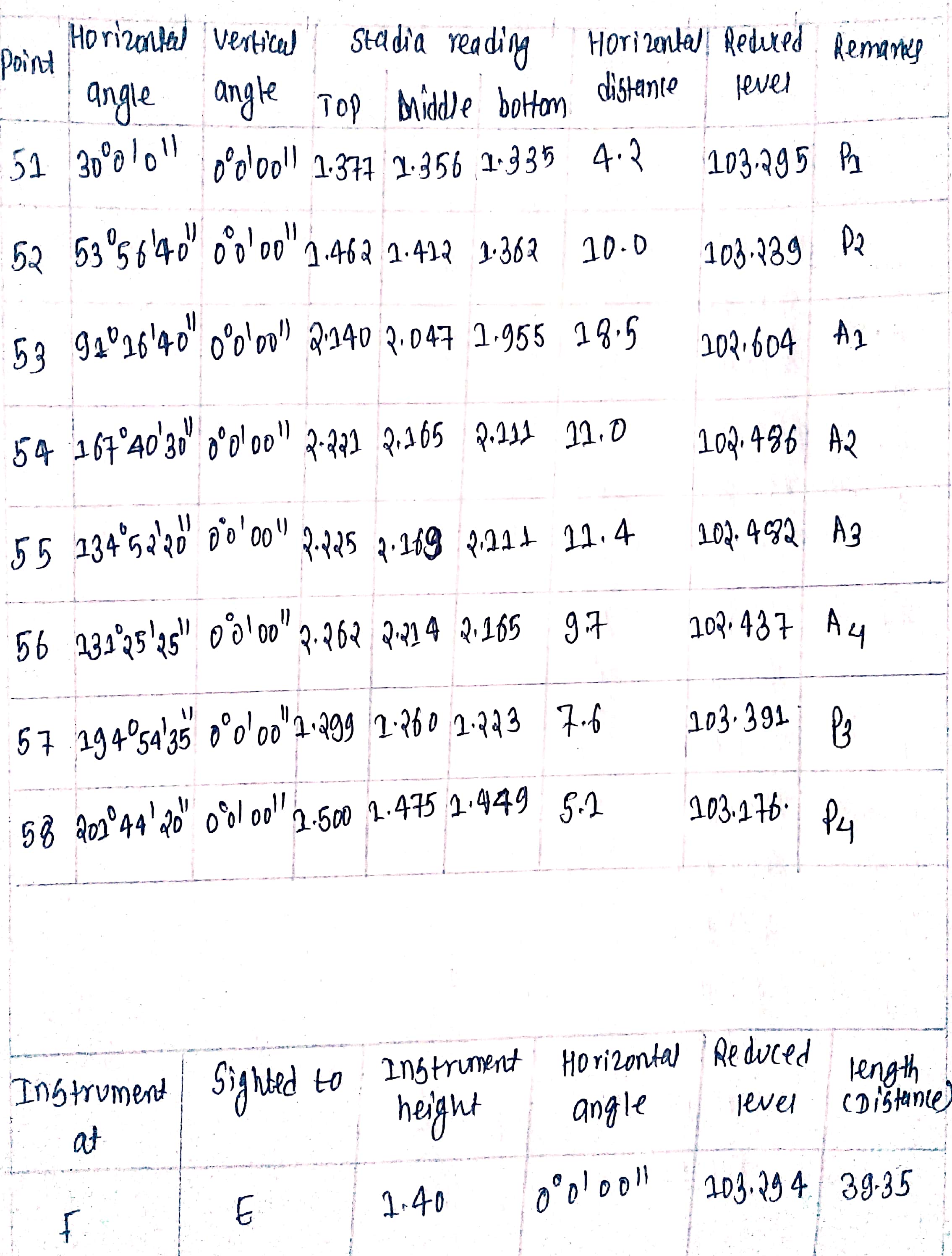
OBSERVATIONS AND CALCULATIONS:
PLOTATION
We will upload this part as soon as possible.
RESULTS:
Hence, a simple topographic map was plotted.
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, we have achieved the objectives of this laboratory which are to introduce the traditional technique of collecting the stadia data such as stadia readings to plot a topographic map and to plot a simple topographic map. From this laboratory activity, we had learnt how to use the theodolite and also familiar with the apparatus. We also get the experience to conduct this laboratory which is stadia tacheometry. We also get the knowledge on how to take the readings of top, bottom and middle of stadia hairs and also the reading of the vertical and horizontal bearings.
 Guest
Guest