Chapter:
1. Explain Factors affecting effective stress,
The pressure transmitted through grain to grain at the contact point through a soil mass is termed as intergranular or effective pressure. It is known as effective pressure since this pressure is responsible for the decrease in the void ratio or increase in the frictional resistance of soil mass.
If the pores of a soil mass are filled with water and if a pressure induced into the pore water tries to separate the grains, the pressure is termed as pore water pressure or neutral stress. The effect of this pressure is to increase the volume of decrease the frictional resistance of the soil mass.
Factors affecting effective stress:
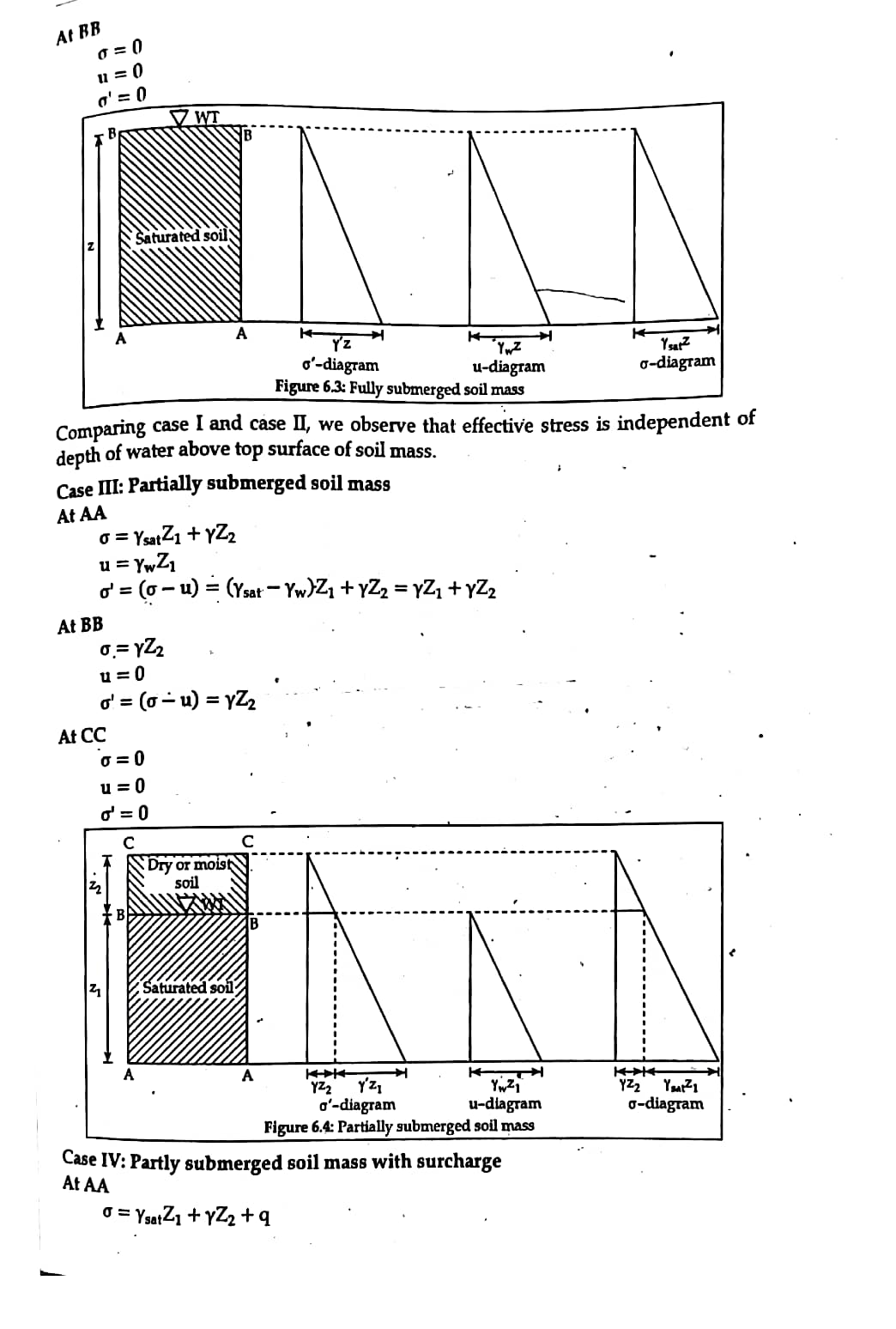
1. Fluctuation on water table.
2. Hydrostatic condition.
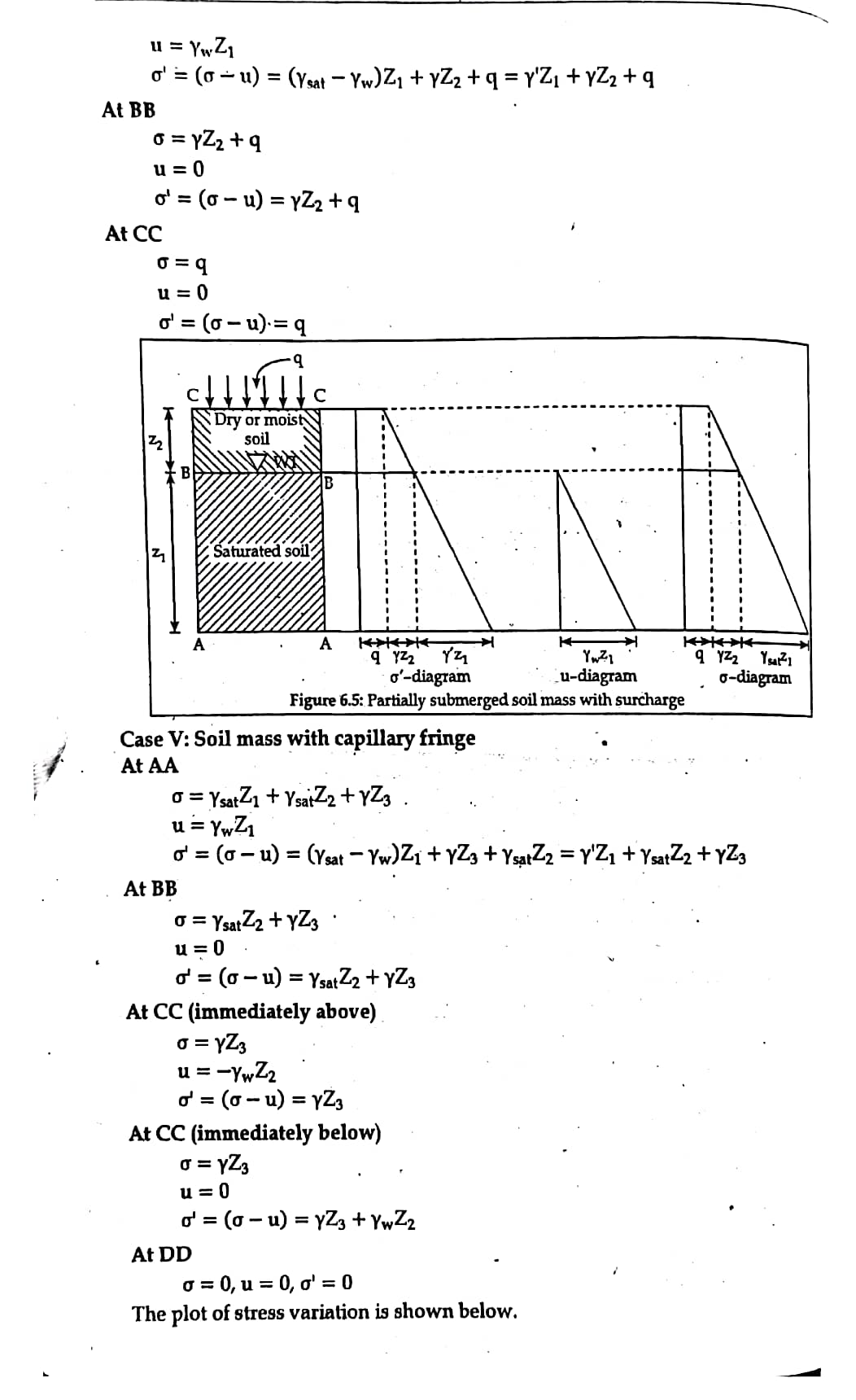
3. Surcharge load.
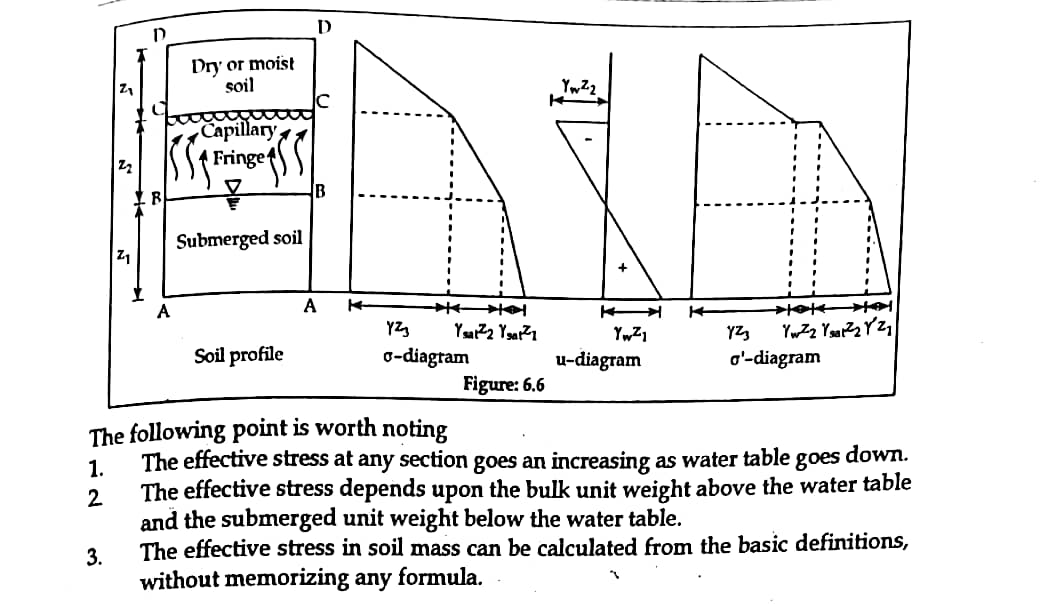
4. Soil saturated by capillary action.
5. Seepage condition.
6. Quick sand condition.
Effect of water table on effective stress:
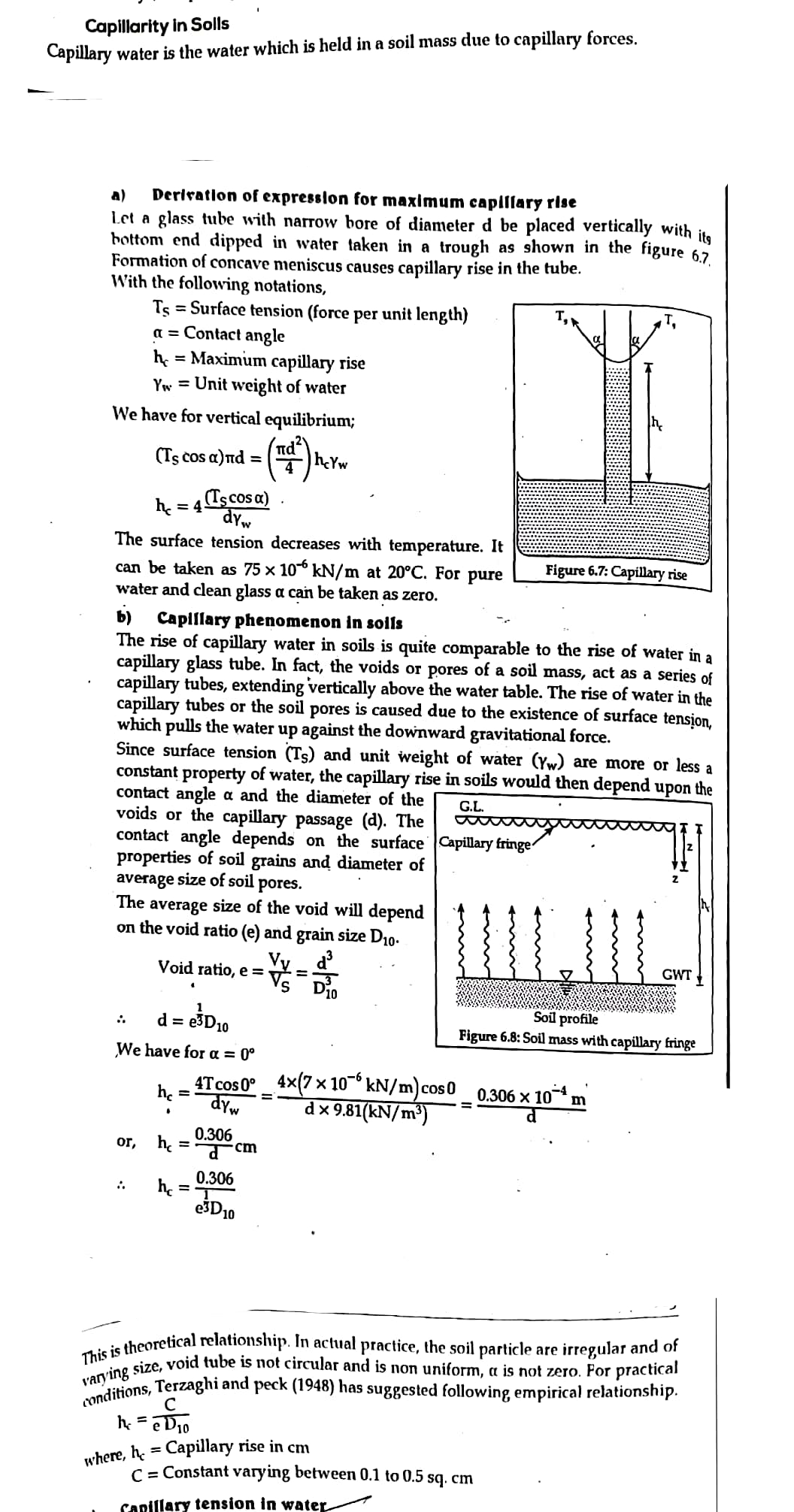
2. Explain Capilirity in soil.
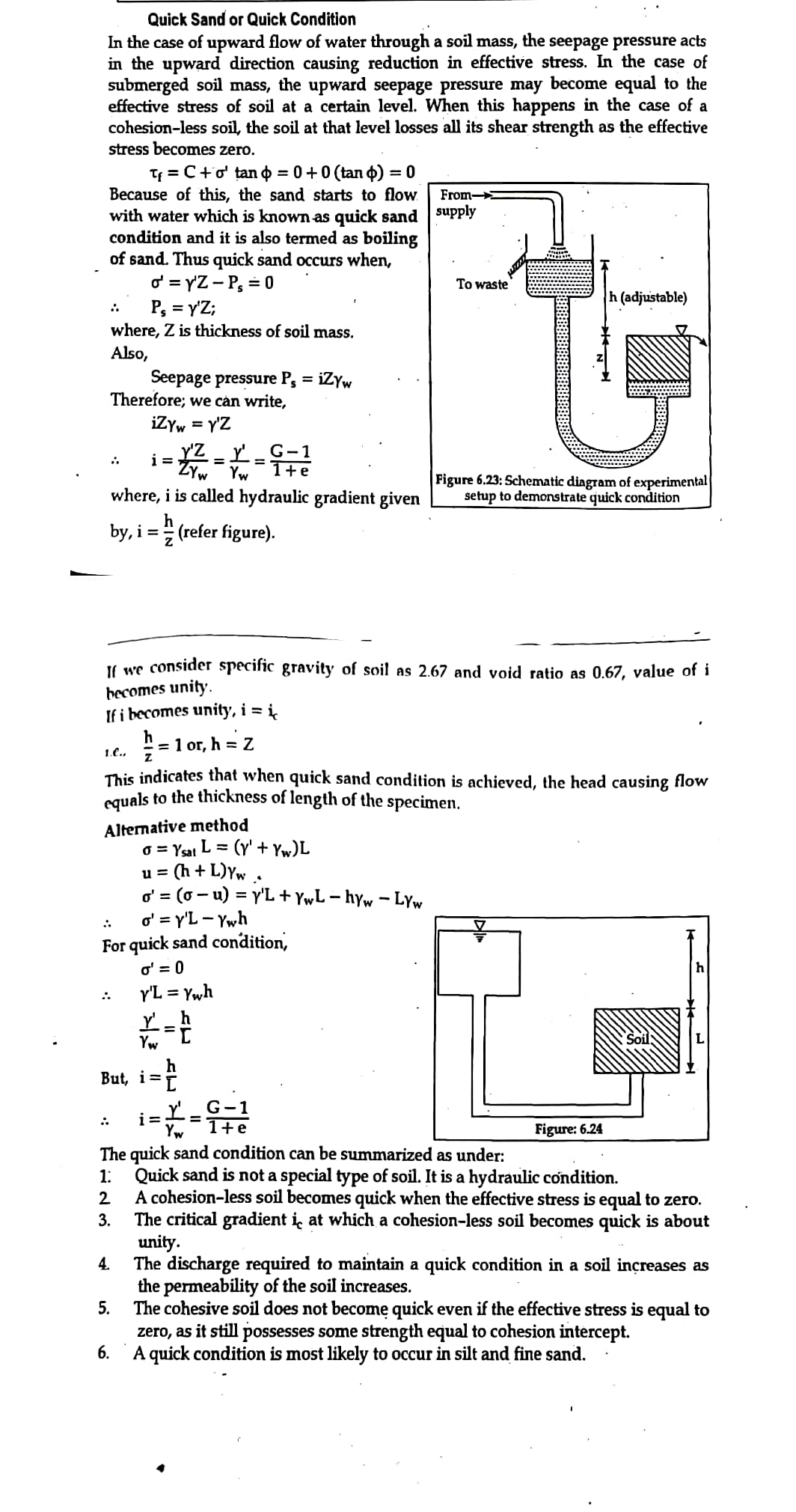
3. Briefly explain Quick sand Condition
How Quicksand Condition Occurs?
Quicksand condition occurs when seepage pressure, which acts in the upward direction, overcomes the downward direction pressure due to
Quicksand Condition at Construction Site
There are a number of construction sites which are susceptible to quicksand conditions:
- Excavations in granular materials behind cofferdams alongside rivers.
- Any place where artesian pressures exist i.e. where head of water is greater than the usual static water pressure.
- Behind
river embankments to protect floods.
How to Avoid Quicksand Condition?
It can be prevented by lowering the water table at the site before excavation or alternatively, by increasing the length of upward flow. Boiling condition is also common when a pervious sand stratum underlying a clay soil is in an artesian pressure condition.
 Guest
Guest